All published articles of this journal are available on ScienceDirect.
Asenapine as a Potential Lead Inhibitor against Central Ca2+/Calmodulin-Dependent Protein Kinase II: Investigation by Docking Simulation and Experimental Validation
Abstract
Aim:
The aim of this potential repurposing study is to investigate the potential inhibitory activity of asenapine against central nervous system CaMKII isozymes using docking experiments and enzymatic assay.
Background:
The Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII) is a multifunctional protein kinase ubiquitously expressed throughout the brain. Emerging biological data have indicated that inhibiting central nervous system CaMKII isoforms, namely, CaMKIIα and CaMKIIβ, may be a promising therapeutic strategy for the potential treatment of many neurological diseases including schizophrenia, depression, epilepsy, and learning deficit.
Objective:
1- Study the possible attractive interactions of asenapine within the binding sites of the central CaMKII isozymes. 2- Evaluate the inhibitory activities of asenapine against central CaMKII isozymes.
Methods:
Docking experiments of asenapine and other known CaMKII inhibitors were performed. Docking settings were validated using ROC analysis. After that, the inhibitory activities of asenapine against central CaMKII alpha and beta were evaluated by enzymatic assay.
Result:
Docking and scoring experiments of asenapine showed several binding interactions anchoring asenapine within CaMKIIα and CaMKIIβ catalytic sites while enzymatic assay results revealed that asenapine can inhibit CaMKIIα and CaMKIIβ in the micromolar range.
Conclusion:
Our study provides evidence that asenapine can serve as a promising lead for the development of new CaMKIIα and CaMKIIβ inhibitors. Moreover, this study reinforces how the investment in drug repurposing could boost the drug discovery process.
1. INTRODUCTION
Calcium calmodulin-dependent kinase II (CaMKII) is serine/threonine kinase involved in Ca2+ signaling [1]. There are four CaMKII isoforms: α, β, λ, and δ. CaMKII α and β are restricted to the central nervous system while λ and δ are expressed in various peripheral tissues including the heart [2].
It is well-established that calcium regulates many cellular processes. When Ca2+ channels in the plasma membrane are activated or when Ca2+ is released from intracellular storage, cytoplasmic Ca2+ concentrations increase. Calmodulin is a major Ca2+ binding protein in the central nervous system. Once calcium binds to calmodulin the resulting complex can interact with a variety of target proteins and control their activity [3]. This contributes to many neuronal pathways (Fig. 1).
Since CaMKII is primarily expressed in neurons, it controls a wide range of neuronal functions, including neurite extension, cellular transport, cellular morphology, neurotransmitter production, and release. It is interesting to note that each CaMKII isoform has a different function in neural plasticity; CaMKIIα primarily controls synaptic strength, whereas CaMKIIβ regulates dendritic morphology, neurite extension, and synapse number [4, 5].
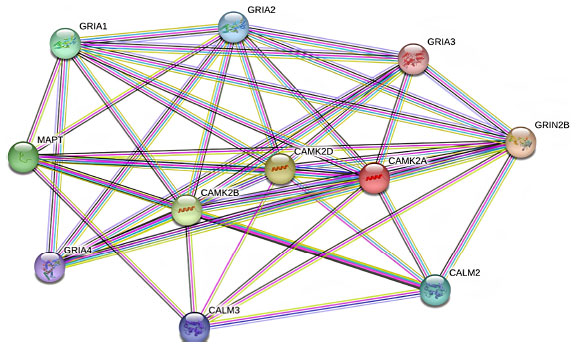
Several studies have demonstrated the diversity of CaMKII interactions with neuronal proteins. However, interactions with various subunits of the glutamate receptor have attracted the most attention [6]. Glutamate AMPA receptors are crucial in maintaining the excitatory synaptic transmission in the central nervous system and influencing many brain functions including cognition, movement, learning, and memory. AMPA receptors are tetrameric assemblies of four subunits encoded by four genes (GRIA1- GRIA4). Phosphorylation of these subunits by CaMKII regulates the function and number of postsynaptic AMPA receptors [7] (Fig. 2).
CaMKII plays important physiological roles in neuronal development and plasticity, and alterations in CaMKII expression/function could contribute to the pathogenesis of many brain disorders [8]. Evidence supports the potential role of CaMKIIβ in the pathophysiology of schizophrenia. Indeed, the prefrontal cortex, a key brain region that is involved in the cognitive symptoms of the disease of patients who had schizophrenia, shows elevated levels of CaMKIIβ transcripts [9, 10]. Likewise, an increase in CaMKIIβ mRNA was found in several animal models of schizophrenia [11].
Epilepsy is among the most dynamic disorders in neurology [12]. Changes in expression and activity of the voltage-gated sodium channel Nav1.6 are the major underlying causes of epilepsy [13]. CaMKII is a strong modulator of Nav1.6 activity and it is critical for neuronal excitability in the brain [14]. Recently, Zybura et al. showed that CaMKII phosphorylates multiple sites on Nav1.6 and inhibiting CaMKII produces a loss-of-function-like phenotype of channel activity; CaMKII inhibition produces decreased Nav1.6 transient and persistent currents, in addition to a right shift in the voltage dependence of activation. Therefore, CaMKII inhibition may represent a promising mechanism to attenuate neuronal excitability in epilepsy [15].
Moreover, CaMKIIβ might be a molecular determinant of depression. In fact, its expression is increased at the mRNA level in the human frontal cortex of depression tissues [10]. Also, at the protein level, CaMKIIβ is significantly upregulated in the lateral habenula (a key brain region in controlling the behavior and pathophysiology of depression) of animal models of depression. Increasing CaMKIIβ is sufficient for producing depressive symptoms. Conversely, antidepressant treatment downregulates this protein and reverses depressive symptoms [16].
Furthermore, CaMKII α and β play a key role in long-term memory induction and learning [17]. The learning deficit depends on long-term memory storage, presumably through a mechanism involving the synthesis of new proteins. Subsequent experiments have shown that the learning deficit is susceptible to disruption via protein synthesis inhibition [18]. Baumbauer et al. reported that CaMKII inhibition is beneficial in preventing the learning deficit observed in spinal rats after non-contingent shock administration [19]. Importantly, administration of CaMKII inhibitor at clinically relevant time points after cardiac arrest provides both neuroprotection and long-term functional benefits. In addition to reducing cell death, CaMKII inhibition also protects the surviving neurons from functional plasticity impairments and prevents behavioral learning deficits [20].
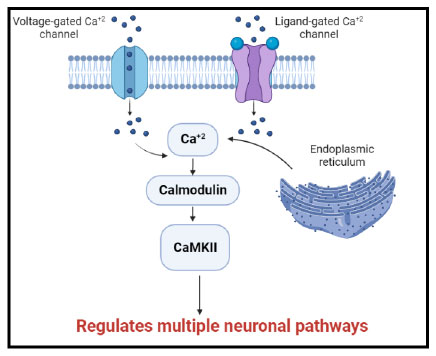
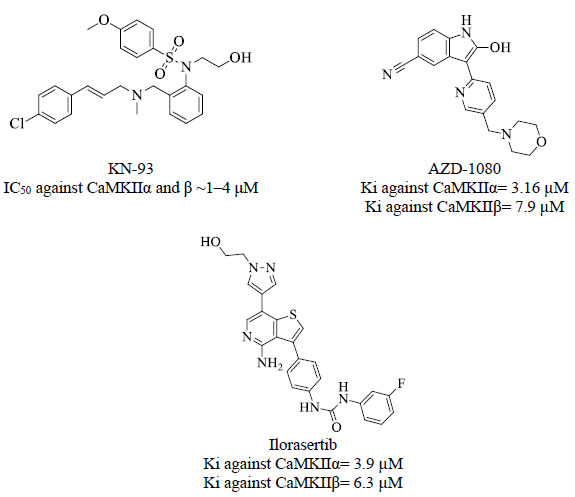
These converging findings highlight the clinical potential for inhibition of central CaMKII and point to this kinase as an attractive target for drug discovery efforts. To date, there is no drug targeting CaMKII in clinical use [21]. Only two inhibitors have been most widely used in research, including the selective small-molecular allosteric inhibitor KN-93 [21] and the peptide inhibitor TatCN21 which is composed of 21 amino acids [22]. Fig. (3) shows some inhibitors against CaMKII α and β extracted from the ChEMBL database [23].
The fact that the discovery and development of new drugs are a long and expensive process with a high attrition rate [24] underlines why drug repurposing can be a more efficient alternative, compared with the traditional approach [25]. Drug repurposing represents an attractive and promising option to identify possible treatment strategies using already FDA-approved marketed drugs. Obviously, the repurposing of such drugs against today’s diseases involves the use of de-risked compounds regarding safety and pharmacokinetic properties with potentially lower overall costs and shorter development timelines [25-28].
Computer-aided drug design and discovery (CADD) techniques have become crucial for drug discovery in order to facilitate drug development in a more affordable way and minimize failures in the final stage. CADD is applying computational methods to rationalize the discovery, design, optimization and development of new drug molecules. CADD can be categorized into two major domains: Ligand-based and Structure-based drug design [29, 30].
Ligand-based drug design techniques depend on the identification of structural and physiochemical similarities among potent ligands that are strongly related to their biological affinity [31]. On the other hand, structure-based methods rely on X-ray crystallographic structures of targeted receptor/ligand complexes and use the interactions perceived within receptor-ligand complexes to generate binding models and utilize them in the discovery and optimization of new bioactive compounds [32, 33]. Molecular docking is one of the most established structure-based methods that predict the potential binding of a compound in a certain target and estimates affinity based on complementarities between the shape and electrostatics of the binding site surfaces and the ligand [34].
Drug repurposing studies can be carried out either by experimental screening approaches using high-throughput assays or by in silico approaches employing computational methods that are low-priced than the former. Virtual screening is a promising CADD technology and plays a key role in repurposing studies. It can be classified as receptor-based screening and ligand-based screening. Herein, the receptor-based screening was employed by exploring the affinity of asenapine to the central CaMKII using molecular docking [35].
Asenapine (dibenzo-oxepino-pyrrole, Fig. 4) is an atypical antipsychotic drug that has been approved since 2009 by the US Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of schizophrenia in adults and the treatment of acute manic or mixed episodes of bipolar in both adult and pediatric populations. Asenapine is a tetracyclic drug with antidopaminergic and antiserotonergic activity [36].
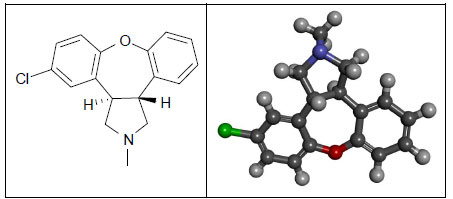
Herein, we investigated the potential inhibitory activity of asenapine against central nervous system CaMKII isozymes as a potential repurposing study using docking experiments and enzymatic bioassay in comparison with known CaMKII inhibitors.
2. MATERIALS AND METHODS
2.1. Docking Study
A docking study was performed using Discovery Studio (version 4.5, BIOVIA, USA). The 3D coordinates of human CaMKIIα and CaMKIIβ were downloaded from the Protein Data Bank (B subunits of 2VZ6 and 3BHH, respectively). Both proteins were prepared by first deleting alternate conformations. In the 2VZ6 case, three alternate conformations for CYS289, HIS76, and VAL73 were deleted. No alternate conformations were found in 3BHH. After that, incomplete amino acid residues were completed and energy was refined. In the 2VZ6 case, the following amino acids were completed and energy refined: Leu-5, Gln-2, Leu34, Lys47, Glu82, Glu216, Arg296, and Lys300. In the 3BHH case, the following were completed and refined: Thr11, Asp12, Ile20, Lys22, Ser26, Arg29, Lys33, Lys48, Lys49, Arg53, Gln56, Lys57, Glu59, Glu83, Glu106, Tyr107, Lys138, Lys147, Lys149, Gln165, Asp167, Gln168, Phe174, Arg187, Lys188, Glu189, Trp215, Glu217, Lys221, Lys227, Lys246, Ile255, Lys259, Glu265, Lys268, Met281, Glu286, Lys292, Lys293, Arg297, Arg298, Lys299, Leu300, and Lys301. Then loops were added and minimized. In the 2VZ6 case, no loops were added. In the 3BHH case, loop Gly23-Ala24-Phe25 was added and minimized. Bonds and bond orders were checked and corrected if necessary. Finally, hydrogen atoms were added to the proteins utilizing Discovery Studio 4.5 templates for protein residues.
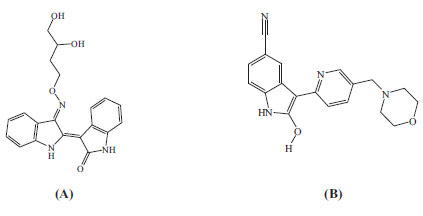
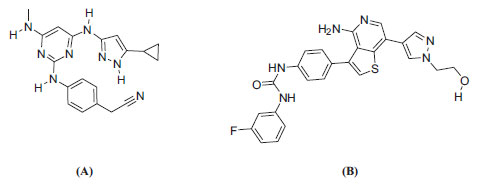
The resulting protein structures were utilized in subsequent docking experiments without further energy minimization. Explicit water molecules were kept in the binding pockets. Asenapine, AZD-1080, and ilorasertib (Figs. 5 and 6) were ionized and docked into the binding pockets of CaMKII-α and CaMKII-β (defined from the co-crystallized bound ligands FEF and 5CP, respectively) using a LibDock docking engine.
The site-feature docking algorithm (LibDock) [37, 38] docks ligands, after removing their hydrogen atoms, into a putative active site guided by binding hotspots. The ligands' conformations are aligned to polar and apolar receptor interaction sites (i.e., hotspots). Conformations can be either pre-calculated or generated on the fly. A CHARMm minimization step can be optionally enabled to further optimize docked poses [37, 38].
LibDock docking takes the following steps. (i) Remove hydrogen atoms. (ii) Rank ligand conformations and prune by solvent-accessible surface area (SASA). (iii) Find hotspots using a grid that is placed into the binding site and use polar and apolar probes. The numbers of hotspots are pruned by clustering to a user-defined value. (iv) Dock ligand poses by aligning to binding site hotspots. This is performed by using triplets (i.e., three ligand atoms are aligned to three receptor hotspots). (v) Pose which results in protein clashes are removed. (vi) Perform a final BFGS pose optimization stage using a simple pair-wise score (similar to Piecewise Linear Potential). The top scoring ligand poses are retained. (vii) Add back hydrogen atoms to the docked ligands. (viii) Optionally, carry out CHARMm minimization to reduce steric clashes caused by added hydrogen atoms [37, 38].
The following LibDock parameters were implemented in the current study. Prior to docking, the DiscoveryStudio 4.5 module CAT-CONFIRM was used to generate a maximum of 250 conformers (not exceeding an energy threshold of 20 kcal/mol from the most stable conformer) for each ligand employing the “CAESAR” conformation generation option. Binding site spheres of 5.0 Å and 7.0 Å radii surrounding the centers of the co-crystallized ligands of CaMKII-α and CaMKII-β, respectively (PDB codes FEF and 5CP, respectively, Figs. 5 and 6) were used to define the binding site for docking. The number of binding site hotspots (polar and apolar) was set to 100. The ligand-to-hotspots matching RMSD tolerance value was set to 0.60 Å and 1.0 Å, for CaMKII-α and CaMKII-β, respectively. The maximum number of poses saved for each ligand during hotspot matching before final pose minimization was set to 100. The maximum number of poses to be saved for each ligand in the binding pocket was 100. The minimum LibDock score (poses below this score are not reported) was 100. The maximum number of rigid body minimization steps during the final pose optimization (using BFGS method) was 50. The maximum number of steric clashes allowed before the pose-hotspot alignment is terminated (specified as a fraction of the heavy atom count) was 0.1. The maximum value for nonpolar solvent accessible surface area for a particular pose to be reported as successful was 15.0 Å2. The maximum value for polar solvent accessible solvent area for a particular pose to be reported as successful was 5.0 Å2. Docked poses/conformers were energy-minimized in situ after docking to remove any receptor/ligand clashes. In the current research, each docked pose was minimized over 1,000 steps of the steepest descent minimization with RMS gradient tolerance of 3 kcal/(mol x Å), followed by conjugate gradient minimization with RMSD cutoff of 1.0 Å, minimization RMS gradient of 0.001 kcal/(mol x Å), and minimization energy change of 0.0 kcal.
2.2. Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) Curve Analysis
The docking study was validated using ROC curve analysis [39-41]. The ROC testing sets were composed of experimentally validated active and inactive CaMKIIα and CaMKIIβ inhibitors extracted from the ChEMBL database [23]. The ROC set of CaMKIIα includes 20 active compounds (Ki < 800 nM) and 110 inactive compounds (Ki > 3,900 nM). On the other hand, the ROC set of CaMKIIβ includes 20 active compounds (Ki < 800 nM) and 104 inactive compounds (Ki > 7900 nM). Each list is docked into its corresponding binding site using the same parameters of the docking experiment (see section 2.1). Subsequently, LibDock scores were evaluated in their abilities to distinguish active members from inactive compounds. The area under the curve (AUC) was used as a success criterion. In the current project, we implemented the “ROC Curve” node within KNIME Analytics Platform (Version 4.5.2) for ROC analysis.
2.3. CaMKII Inhibitory Enzymatic Assay
Asenapine (As asenapine maleate (Form-L), 99.8% w/w purity) was kindly gifted from Hikma Pharmaceuticals, Amman, Jordan. Bioassays were performed against CaMKII isoforms (CaMKIIα and CaMKIIβ) using Invitrogen's Z'-LYTE® fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) kinase assay kit [42] based on donor (coumarin) and acceptor (fluorescein) fluorophores labeled on synthetic substrate peptide [43]. Stock solutions of asenapine were prepared in DMSO, and then serially diluted in buffer solution provided within the assay kit to yield final concentrations ranging from 1 μM to 500 μM. DMSO did not exceed 1% in the final kinase reaction. ATP was used as a substrate at Km concentrations for the two isoforms (10 µM and 75 µM for CaMKIIα and CaMKIIβ, respectively). The settings of the assay were validated using staurosporine as the positive control (IC50 values 0.62 nM and 0.59 nM against CaMKIIα and CaMKIIβ, respectively) and provided a buffer solution as the negative control. The concentration required to give 50% inhibition (IC50) was determined from the dose-response curves at 5 asenapine concentrations (500 μM, 100 μM, 50 μM, 10 μM, and 1 μM). Measurements were repeated in duplicates.
3. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The escalating cost and length of time required for new drug development have made drug repurposing a valuable strategy for identifying new uses for approved drugs [26, 44, 45]. Asenapine is a second-generation atypical antipsychotic drug [46]. It is approved for acute schizophrenia and bipolar disorders and as an adjunctive therapy with lithium or valproate [47]. Although the exact mechanism of action of asenapine is unknown [48, 49], it has been shown to have antagonistic activity against a wide range of receptors, including serotonin receptors, α-adrenoceptors, and dopamine receptors [50], through which it presumably mediates some of its pharmacological activity [51]. On other hand, CaMKII plays important physiological roles in the central nervous system [8, 52]. Several studies demonstrated that overexpression of this kinase could contribute to the pathogenesis of many brain disorders such as schizophrenia, depression, epilepsy, and learning deficit [8-20]. Therefore, CaMKII inhibition may represent a promising mechanism for the management of these disorders. Accordingly, we decided to evaluate the potential inhibitory effect of asenapine against central CaMKII isozymes, CaMKIIα and CaMKIIβ, in an attempt to repurpose this drug for epilepsy and learning deficit management in addition to its well-established role in schizophrenia and depression. Towards this end, docking experiments and enzymatic assay were carried out.
Initially, we compared asenapine with known micromolar CaMKII inhibitors vis-à-vis docking poses and scores. In the CaMKIIα case, we compared asenapine with AZD-1080 (Fig. 5, reported Ki = 3.16 µM in the ChEMBL database [23]). However, in the CaMKIIβ case, we compared asenapine with ilorasertib (Fig. 6, Ki = 6.3 µM, as in ChEMBL database [23]). We also compared docked asenapine with the corresponding co-crystallized bound ligands in each CaMKII isozyme (both ligands are nanomolar inhibitors of their corresponding CaMKII isozymes).
However, before proceeding with the docking experiment, it was necessary to validate the docking settings by comparing the crystallographic poses of complexed ligands (FEF and 5CP complexed within CaMKIIα and CaMKIIβ, respectively) with their corresponding docked poses. The Libdock docking engine [37, 38] closely reproduced the crystallographic poses of FEF (in CaMKIIα, Fig. 7) and 5CP (in CaMKIIβ, Fig. 8) with root mean square difference (RMSD) values of 1.10 Å and 0.86 Å, respectively.
Moreover, ROC analysis was performed to validate the docking study where lists of inactive compounds seeded with a limited number of active CaMKIIα and CaMKIIβ inhibitors were docked into their corresponding binding pockets using the same docking experiment settings. Then the LibDock score was used as a classification factor to distinguish active from inactive. Evidently, ROC illustrated good classification performance with AUC 0.67 and 0.63 for CaMKIIα and CaMKIIβ, respectively (Fig. 9). These results provided the impetus to proceed in docking asenapine and other inhibitors into CaMKIIα and CaMKIIβ using the same settings.
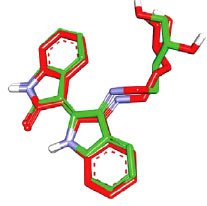
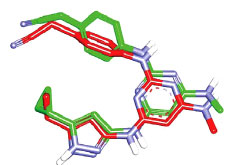
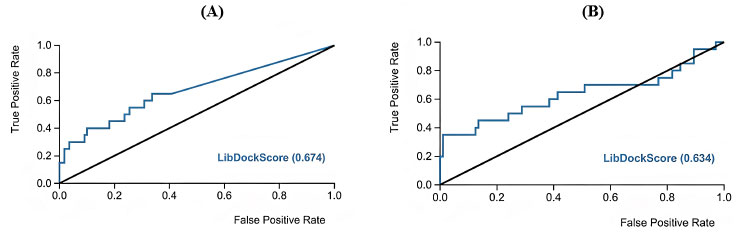
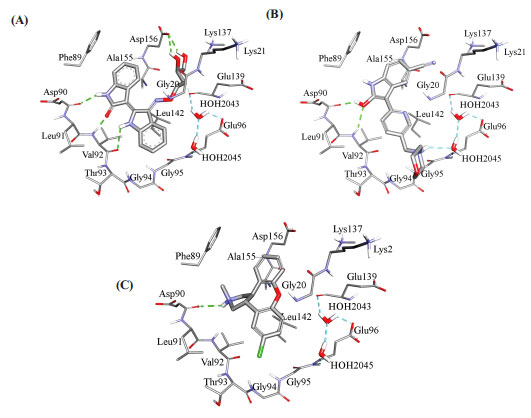
Fig. (10) compares binding interactions anchoring co-crystallized FEF within the CaMKIIα binding site with those proposed by docked AZD-1080 and asenapine. FEF binding involves three hydrogen-bonding interactions with the hinge region of CaMKIIα (Fig. 10A): the indolone NH and carbonyl with the peptidic carbonyl and NH of hinge Asp90 and Val92, respectively, and the dihydroindole NH with the peptidic carbonyl of Val92. Moreover, the terminal glycol hydroxyls of FEF are hydrogen-bonded with COOH of Asp156 (Fig. 10A). In contrast, docked AZD-1080 is anchored to the CaMKIIα hinge region via two hydrogen bonds anchoring the indole hydroxyl of AZD-1080 to the peptidic carbonyl and NH of Asp90 and Val92, respectively, as in Fig. (9). Additionally, the morpholino ammonium of docked AZD-1080 is hydrogen bonded to the peptidic carbonyl of Glu139 and the carboxylic acid of Glu96 via two bridging water molecules, i.e., H2O2045 and H2O2043, as in Fig. (10B). However, the docked pose of asenapine involves only one hydrogen bonding interaction with the hinge region of CaMKIIα connecting the cationic NH of asenapine’s pyrrolidine ring with the peptidic carbonyl of Asp90, as in Fig. (10C).
Hydrophobic and π-stacking interactions are also noted in the crystallographic and docked complexes in Fig. (10). In the case of FEF, Fig. (10A), the dihydro-indole stacks against the peptidic amide connecting Gly94 to Gly95 and is placed at close proximity to Leu142, suggesting mutual π-stacking and hydrophobic interactions, respectively. Additionally, the indolone ring π-stacks against the aromatic side chain of Phe89. Likewise, AZD-1080 exhibits a similar stacking interaction between the cyanobenzene ring and the aromatic side chain of Phe89 while the pyridine fragment is docked close to Leu142 suggesting mutual hydrophobic attraction (Fig. 10B). Similarly, in the asenapine case, the unsubstituted benzene wing of asenapine is placed in close proximity to the phenyl side chain of Phe89 suggesting mutual π-stacking interactions (Fig. 10C) while the chlorobenzene wing π-stacks against the peptide amide linking Gly94 with Gly94 (Fig. 10C).
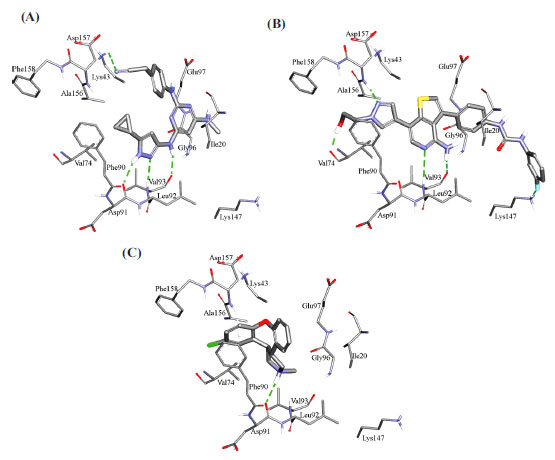
Fig. (11) compares the binding interactions tying co-crystallized ligand 5CP into the CaMKIIβ binding site with those proposed by the docking study for ilorasertib and asenapine into the same target. 5CP is anchored to the binding pocket of CaMKIIβ via four hydrogen bonds (Fig. 11A): the pyrazole NH and sp2 nitrogen with the peptidic carbonyl and NH of Asp91 and Val93, respectively, the pyrazole-to-pyrimidine NH linker with the peptidic carbonyl of Val93, and the terminal cyano with the side chain ammonium of Lys43 (Fig. 11A). Moreover, the cyclopropyl of 5CP is close to the aromatic ring of Phe90 (4.0 Å) suggesting mutual hydrophobic attraction.
Likewise, the docked pose of ilorasertib (Fig. 11B) shows hydrogen-bonding interactions connecting its central 2-aminopyridine with the backbone peptidic NH and carbonyl of hinge Val93. Also, the terminal hydroxyl and pyrazole sp2 nitrogen of ilorasertib is hydrogen-bonded to the backbone carbonyl and NH of Val74 and Asp157, respectively. At the opposite terminal of the ligand, however, the fluoro of the fluorobenzene is also hydrogen-bonded to the ammonium of Lys147. Additionally, the docked pose of ilorasertib apparently involves π-stacking interaction anchoring the ligand’s pyrazole against the phenyl of Phe90.
On the other hand, the docked pose of asenapine (Fig. 11C) is anchored via single hydrogen bonding interaction connecting its cationic pyrrolidine nitrogen with the backbone carbonyl of hinge Asp91. This cationic center is placed at 7.8 Å from the carboxylate of Asp91 suggesting a certain mutual electrostatic attraction. The chlorobenzene of asenapine is projected between the aromatic side chain of Phe90 and the peptidic amide connecting Ala156 with Asp157 suggesting mutual π-stacking interactions. Interestingly, the unsubstituted aromatic wing of asenapine is also docked close to the aromatic ring of Phe90 indicating additional π-stacking (Fig. 11C).
Tables 1 and 2 show LibDock scores calculated for docked and co-crystallized ligands. LibDock scores combine scores for Van der Waals forces, H-bonds, pi interactions, and other parameters and correlate with binding energy measurements [53].
| Ligand | LibDock Score (KJ/mol) |
|---|---|
| FEFa | 109.53 |
| AZD-1080b | 85.64 |
| Asenapineb | 57.75 |
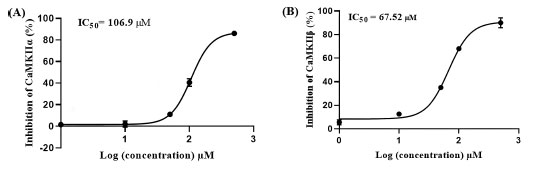
These results suggest asenapine has moderate micromolar inhibitory profiles against CaMKII enzymes encouraging us to assess asenapine using enzymatic assays. Fig. (12) shows the dose-response curves of asenapine against both isozymes. Clearly, asenapine inhibits CaMKIIα and CaMKIIβ at IC50 values of 106.90 ± 12.51 and 67.52 ± 23.42 μM, respectively. Based on the Cheng-Prusoff equation, these values correspond to Ki values of 53.52 and 33.80 μM (ATP was provided at Km concentrations), respectively [54], thus placing asenapine within approximately one order of magnitude from AZD-1080 against CaMKIIα (Ki = 3.16 µM) and ilorasertib against CaMKIIβ (Ki = 6.30 µM).
This inferior inhibitory profile of asenapine compared to AZD-1080 and ilorasertib can be easily justified by the lesser hydrogen bonding that anchored asenapine within the binding site of CaMKIIα and CaMKIIβ as stated in Figs. (10 and 11) respectively, and consequently the lesser docking scores of asenapine (Tables 1 and 2). Given that hydrogen bonding interactions are significant stabilizing factors in ligand–receptor binding [55], missing these interactions in asenapine explains its mediocre inhibitory profile compared to AZD-1080 and ilorasertib.
Still, this research provides evidence for the inhibitory activity of asenapine against central CaMKII isozymes, and this offers an excellent opportunity for further optimization into valid CaMKII inhibitor drug candidates to be used in epilepsy and learning deficit management and as a neuroprotective drug after cardiac arrest in addition to its well-known role as antipsychotic medication.
4. CONCLUSION
The central nervous system CaMKIIα and CaMKIIβ have been identified as valuable targets for the treatment of diverse neurological disorders. A repurposing study using molecular docking and enzyme assay was employed. This study revealed, for the first time, micromolar inhibitory activities of asenapine against central CaMKII isozymes and this highlighted asenapine as a potential lead compound that can be optimized into promising central CaMKII inhibitors. Our docking study pointed to the significance of hydrogen bonding for potent central CaMKII inhibitors suggesting that the future optimization of asenapine requires additional molecular fragments capable of forming extra hydrogen bonds with the binding pockets of these two enzymes.
LIST OF ABBREVIATIONS
| CADD | = Computer-Aided Drug Design and Discovery |
| SASA | = Solvent Accessible Surface Area |
| ROC | = Receiver Operating Characteristic |
| AUC | = Area Under the Curve |
ETHICS APPROVAL AND CONSENT TO PARTICIPATE
Not applicable.
HUMAN AND ANIMAL RIGHTS
Not applicable
CONSENT FOR PUBLICATION
Not applicable.
AVAILABILITY OF DATA AND MATERIALS
Not applicable.
FUNDING
The study is funded by the Deanship of Scientific Research at Applied Sciences Private University, Amman, Jordan.
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors thank the Deanship of Scientific Research at Applied Sciences Private University, Amman, Jordan, for funding this research.


