All published articles of this journal are available on ScienceDirect.
Synthesis of Medicinally Important Indole Derivatives: A Review
Abstract
Indoles constitute a widely occurring functional group in nature and are present in an extensive number of bioactive natural products and medicinally important compounds. As a result, exponential increases in the development of novel methods for the formation of indole core along with site-specific indoles have been established. Conventional methods for the synthesis of indoles are getting replaced with green methods involving ionic liquids, water as a solvent, solid acid catalyst, microwave irradiation and the use of nanoparticles under solvent-free conditions. In addition, there are immense applications of the substituted indoles in diverse fields.
1. INTRODUCTION
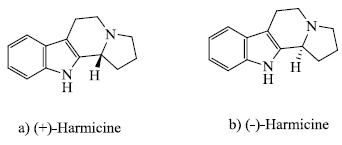
The study of heterocyclic compounds has become a major topic today as most of the natural compounds are essentially heterocyclic compounds. Among the heterocycles, indole-based compounds have immense applications in the field of pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, dyestuff, etc. [ 1 ]. Indole derivatives are widely used as anti-inflammatory [ 2 ], anti-microbial, anti-viral, anti-cancer, antirheumatoidal, anti-HIV, and anti-tumor drugs, as well as corrosion inhibitors, copolymers and sanitizers [3-12]. Compounds like 2-aroylindole [13], 2,3-diarylindole [13], 2-aryl-3-arylcarbonylindole [13], indole-3-carbinol [14], di-indol-3-yl disulfides [15], and hetero-annulated indole derivatives [16] have an indole ring which possesses potential anti-cancer properties. M. Fadaeinasab et al. reported that the indole alkaloid Reflexin A, extracted from Rauwolfia reflexa, possesses anti-cancer properties against HCT-116 cancer cells [17]. Recently, Z.-X. He et al. synthesized new thiosemicarbazone-indole derivatives having anti-cancer properties and low toxic effects [18]. H. Hu et al. designed twelve new substituted indole-2-carbohydrazide derivatives and found that some of them possessed high anti-cancer activity and inhibitory effect on CDK9 while others showed moderate or little such activities [19]. 5-substituted indole derivatives [20], substituted pyrido [3,4-b] indole derivatives [21], indole-7-carboxamides [22], etc. compounds show anti-HIV activities. Other indole-based 4-thiazolidinones and their hydrazones that were synthesized by G. Cihan-Ustundag et al. [23] showed anti-tubercular activities. G. Sanna et al. [24] synthesized 2-(1H-indol-3-yl) ethyl thiourea derivatives that showed promising anti-microbial results. Compounds like indole-3-guanylhydrazone hydrochloride (LQM01) [25], 7-HMIA (7-hydroxyl-1-methylindole-3- acetonitrile) [26], N-substituted indole derivatives [27], chromone-indole derivatives [28], capsaicin-based indole and nitroindole derivatives [29] possess anti-inflammatory activities. Indole ring-based alkaloid [30], Reserpine, extracted from Rauwolfia serpentine is antihypertensive in nature. A plant growth hormone, Auxin (Indole-3-acetic acid), is essential for growth in plants through cell division [31] and exhibits a significant role in the transport of water under drought conditions [32]. Biopolymeric hydrogels based on Auxins [33] have anti-microbial and anti-oxidant properties. Melatonin (an indole derivative) and its analogues also exhibit antioxidant properties [34]. Indomethacin, an acyclogeneses-1 inhibitor, is an anti-inflammatory drug which has been used for years [35]. Harmicine, an alkaloid containing indole nucleus, possesses antileishmanial and antinociceptive properties [36]. C. Sanaboina et al. [37] reported the synthesis of indole-based compounds (±)-harmicine (Fig. 1). M. Sayed et al. synthesized indolylthienopyrimidine derivatives that are thermally stable and have the ability to exert anti-microbial activities [38]. Indigo is probably the oldest and the most famous colorant based on indole. Dyes based on indigo moiety like Vat blue 4B [39], indirubin [39], 6,6′-dibromoindigo [39] have already been commercialized. Indigo carmine (an indole derivative) or sodium salt of 5,5’-indigodisulfonic acid is used as a food colorant [40]. E. Keles et al. synthesized indole-based push-pull dyes containing dimethine and azo chromophores in the same structure were characterized by Fourier Transform Infrared (FT-IR), nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), and mass spectrometry [41]. Donor system (π-acceptor-π-donor-D-π-A-π-D) is included in the synthesized dyes containing azo and dimethine chromophores. Triarylmethane and its analogues are widely used in dyes. S. Cheruku et al. [42] synthesized triarylmethane derivatives which are medicinally important by reacting indoles and benzhydrols. Y.F. Liu et al. extracted five new isatindigotindoloides (indole alkaloid glucosides) extracted from Isatis indigotica roots, three out of which have shown antiviral properties against the influenza virus [43]. A.-H. Chen et al. reported the isolation of 10-methoxyakuammidine (a monoterpenoid indole alkaloid) having anti-cancer properties against human cancer cells [44]. N-formylserotonin, along with five other indole alkaloids, was isolated by Y.-H. Dai et al. from Chinese medicine Chansu [45]. Out of those six alkaloids, only Bufoserotonin C was found to have a cytotoxic effect against human lung adenocarcinoma epithelial cells. There are several indole alkaloids isolated from plants like Aegiceras corniculatum [46], Cimicifuga heracleifolia [47], Murraya paniculata [48], and Acanthus ilicifolius [49]. Y. Chang et al. devised indole-based IHT probe for the detection of Cu(II) ion. This low-cost probe shows visible colour change to naked eyes [50]. S. Li et al. synthesized poly(indoles) that can act as conducting polymer, energy storage and also can detect Fe(III) ion [51]. Y. Tang et al. [52] designed a highly specific and sensitive light-up fluorescent probe to detect Hg(II) ions based on indole-rhodamine fluorophore. A. Hanna-Elias et al. [53] showed that indole-3-methanamine and its derivatives can act as ligands for 5-HT4 receptor. A. Kathiravanet al. [54] reported that indole attached with rhodanine-3- acetic acid group is an efficient compound for the dye-sensitized solar cells, and hence acts as an excellent light harvester. M. Zhang et al. synthesized 6-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)-1H-indole to develop a non-linear optical chromophore with enhanced properties [55]. X. Zhou et al. synthesized Thieno[3,2-b]indole (TI) bridged molecules that have applications in organic solar cells [56]. Y. Wang et al. synthesized chiral indole-phosphine oxazoline ligands which are useful for allylic alkylation reaction using palladium catalyst [57]. T. Suzuki et al. [58] synthesized substituted indoles, showing good pharmacological properties, in the presence of trichloroacetimidates via Friedel-Crafts alkylation of indoles. H.H. Dib et al. [59] synthesized indole derivatives with excellent biological activities via gas-phase pyrolysis reaction.
Thus, the synthesis of indole and its derivatives is quite interesting. In order to synthesize those compounds, it is very important to follow the Green Chemistry protocols. Green chemistry can be used to develop the reaction in such a manner that reduces or eliminates environmental impacts and generation of hazardous by-products [60]. Developing a reaction using new technologies following the protocols of green chemistry has become an important topic in this field of research.
This review mainly focuses on the synthesis of indole and its derivatives using both conventional and green methodologies.
2. CONVENTIONAL METHODS
2.1. Synthesis of Indole Derivatives from Aromatic Hydrazines
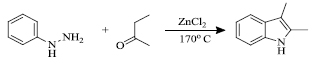
In 1883, this reaction was first reported by Emil Fischer and Jourdan. Here, in the presence of Lewis/mineral acid, arylhydrazones coupled from aromatic hydrazines were reacted with aldehydes or ketones to give indole derivatives [61] (Scheme 1). Cation-exchange resins, toluene sulfonic acid, phosphorus trichloride and acidic clays were used for efficient cyclisation at different temperatures [62]. Electron-withdrawing groups slow down the progression while electron-donating groups available with benzene ring enhance the rate of the reaction.
2.2. Synthesis of Indole Derivatives from 4-(Ethylsulfonyl)-1-Chloro-2-Nitrobenzene
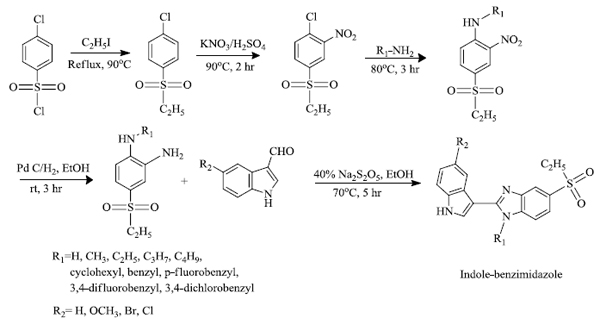
F.Z. Karadayi et al. [63] successfully synthesized indole-benzimidazole derivatives. A total of 37 derivatives of indole-benzimidazole and their anti-cancer activity were studied. Among them, the compounds that had p-fluorobenzyl at the R1 position along with the electron-withdrawing group at R2 were more anti-cancer active compounds than others. Microarray analysis and docking studies reveal that the compounds having p-fluorobenzyl and -Br at R1 and R2 position, respectively, possess prominent activity against MCF-7 cells. The following scheme 2 shows the path for the formation of derivatives of indole-benzimidazole.
2.3. Synthesis of 2-carbomethoxy Indoles Relying on two Heck Arylations of Methyl Acrylate and Nitro Cinnamates, Respectively
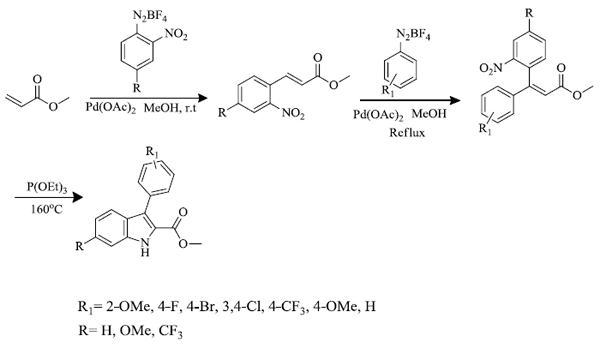
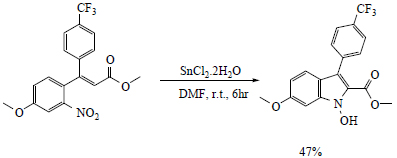
N.M. Cury et al . [ 64 ] synthesized 2-carbomethoxy-3-aryl-indoles by a series of reactions. Firstly, Heck-Matsuda arylation reaction was carried out between methyl acrylate and salts of arenediazonium having a nitro group at ortho position in the presence of palladium acetate catalyst. The nitro cinnamates formed (80-87% yield) were again used to react with arene diazonium salts via Heck-Matsuda reaction in the presence of palladium acetate catalyst (7.5 mol%) in methanol to give 3,3-diaryl acrylate (29-89% yield) which further underwent Cadogan-Sundberg reductive cyclization to give 2-carbomethoxy-3-arylindoles (57-91%), promoted by P(OEt)3 (Scheme-3). Preparation of N-hydroxy indoles(47% yield) was also carried out by reductive cyclization of 3,3-diaryl acrylate in the presence of SnCl2 in dimethylformamide (DMF) solvent (Scheme 4).
2.4. Synthesis of indole derivatives using ruthenium (II) photocatalyst
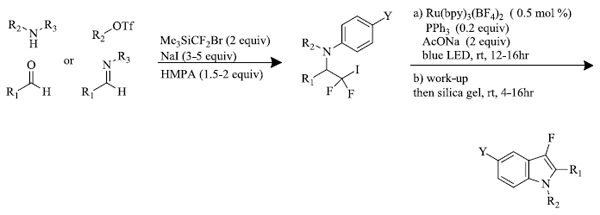
L.I. Panferova et al. [65] synthesized 3-fluoroindole derivatives from difluoroiodomethyl-substituted amines by using Ruthenium (II) photocatalyst along with triphenylphosphine radiated by blue light (Scheme 5). Nucleophilic iodo difluoromethylation of iminium ions provided the required starting material, N-arylamines.
3. GREEN METHODOLOGIES
There are several methods by which the derivatives of indole can be prepared by following the protocols of green chemistry. These are listed as follows:
3.1. Synthesis using Ionic Liquids
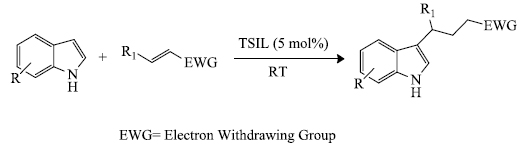
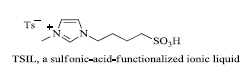
a) At present, researchers have focused their efforts on the use of ionic liquids for the synthesis of indole derivatives. For example, Das et al . [ 66 ] prepared 3-substituted indoles by the use of Michael addition. In this process, a Bronsted acid catalyst, anionic liquid: sulfonic-acid-functionalized (a TSIL, i.e. Task-specific ionic liquid) was used for the effective preparation of 3-substituted indoles (12 examples) in yield ranging from 40-95% (scheme 6 ). The catalyst (Fig. 2 ) could be used up to ten successive times without any notable change in its activity.
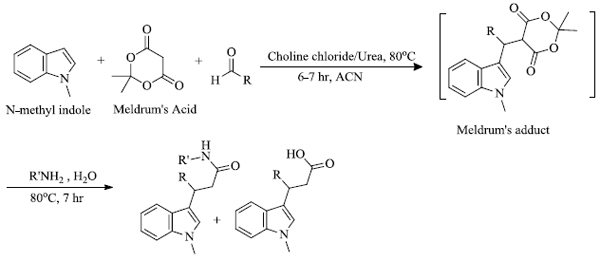
b) E. Siddalingamurthy et al . [ 67 ] developed a sequential method for the preparation of derivatives of indole-3-propanamide by the use of green catalyst choline chloride/urea. Here, N-methyl indole was reacted with Meldrum’s acid and aromatic aldehydes that resulted in the formation of an adduct which further provided the required product in the presence of an amine (Scheme 7 ). The method is advantageous as it involves simple operation, reduced reaction time and ease of isolation of products.
c) Y. Du et al. [68] via [4+2] annulation reaction successfully synthesized carbazole (compound having indole nucleus) derivatives in the presence of Bronsted acid ionic liquid [Bpy]HSO4 (scheme 8). It has been observed that this method encompasses mild and metal-free conditions which are cost-effective for the production of a wide range of carbazole derivatives. The catalyst could be reused without any significant change in its activity.
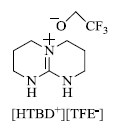
d) C. Li et al. [ 69 ] recently developed pyrano[4,3-b]indol-1(5H)-ones by the use of protic ionic liquids like [HTBD+][TFE-](Scheme 9 ) (Fig. 3 ). The advantages of this method include considerably high yield, easy to conduct reaction work-up and broad substrate scope.
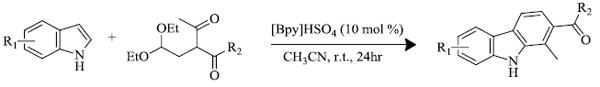
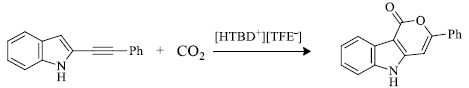
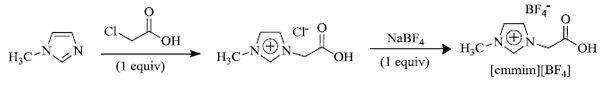
e) F.P. Yi et al. used [cmmim] [BF4] (i.e., 1-carboxymethyl3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate) as the ionic liquid catalyst (synthesis of catalyst shown in Scheme 10 ) for the successful synthesis (Scheme 11 ) of indole derivatives using Fischer synthesis [ 70 ]. The ionic liquid catalyst is eco-friendly, efficient, and can be reused without any prominent change in its activity, and is easily recoverable.
3.2. Additional Green Methods for Synthesis of Various Bioactive Indole Derivatives using Indole as a Precursor
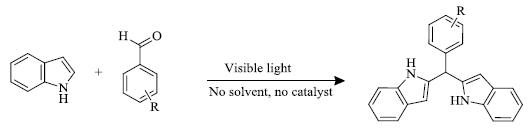
a) B.S. Hote et al . [ 71 ], under solvent and catalyst-free conditions in high yields (80-90%) in time intervals of 30-90 minutes (Scheme 12 ), successfully synthesized indole derivatives by the reaction of various substituted benzaldehydes and indoles under visible light irradiation (irradiation done by 150W Tungsten Lamp). This method is completely green as there is no use of catalyst or solvent, which also makes the process economical.
b) S.A. Sadaphal et al . [ 72 ], under solvent-free conditions, successfully synthesized indole derivatives. The synthesis was performed between indole and substituted aromatic aldehydes by the use of Cellulose Sulfuric Acid (CSA) catalyst (Scheme 13 ). Due to the non-hygroscopic solid nature of the acid, Cellulose sulfuric acid can be used as a catalyst and reused at least twice for this process without any significant change in its catalytic activity, providing a green route for the synthesis.
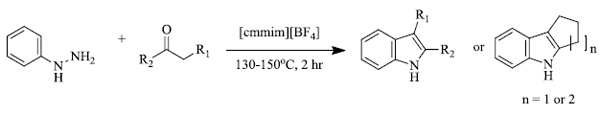

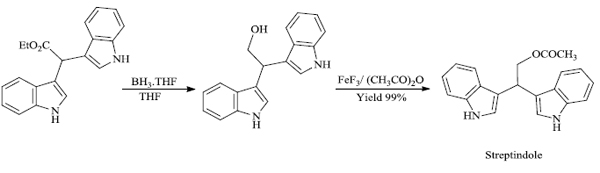
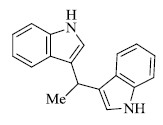
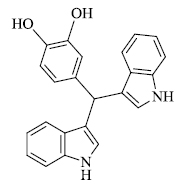
c) R. Surasani et al. [73] prepared certain indole derivatives from the reaction of indole with aromatic/ aliphatic aldehydes using Indion Ina 225h resin catalyst (Scheme 14). The products are obtained in high yield in lesser time and the catalyst is more selective to aldehydes rather than ketones. Along with this, Indion Ina 225H can be reused five times as compared to other catalysts reported in the literature, making the process economically and environmentally favorable. Naturally occurring bis(indolyl)methanes based compounds like Vibrindole A (Fig. 4), 4-(di(1H-indol-3- yl)methyl)benzene-1,2-diol (Fig. 5) and Streptindole (Scheme 15) have also been prepared by the same process.

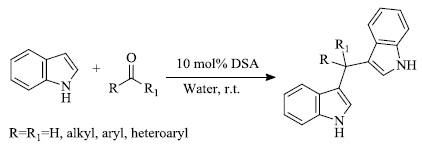
d) P. Hazarika et al . [ 74 ] reported the preparation of indole derivates by the use of water as a solvent. In this process, indole and carbonyl compounds in the presence of the catalyst dodecylsulphonic acid and water as a solvent yield bis(indolyl)methane as the product. (Scheme 16 ). The reaction gets completed in a short time period with a considerably high yield.
3.3. Synthesis of Indole Derivatives Using Water as the Solvent
Various indole derivatives have beenprepared using water as the solvent. Water is a green solvent for many reactions and is more advantageous to use with respect to other solvents in terms of toxicity. Following are the reactions where the synthesis of indole derivatives has been carried out in water:
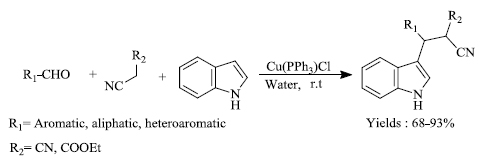
a) A.N. Prasad et al. successfully used multi-component reaction for the preparation of 3-substituted indole [75]. With water as medium, indole along with aldehydes and active methylene compound in the presence of catalyst Cu(PPh3)Cl (Scheme 17) yielded potentially important indole derivatives. The targeted substance was attained in high yield ranging from 68-93%. The high efficiency of the catalyst and the use of water as a medium make the process more economical and eco-friendly.
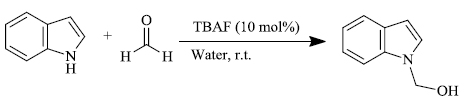
b) H.M. Meshram et al. [76] prepared hemiaminal of indole by the use of phase-transfer catalyst tetrabutylammonium fluoride (TBAF) in water as the medium. In the presence of TBAF, indole and its derivatives reacted with formaldehyde at ambient temperature, producing the corresponding products in yield ranging from 84-96%. The reusability of the reaction media and mild reaction conditions of this process contribute to the protocols of green chemistry. The following (scheme 18) provides a simple path for the synthesis of hemiaminal.
3.4. Synthesis of Indole Derivates - Solid Acid Catalyst
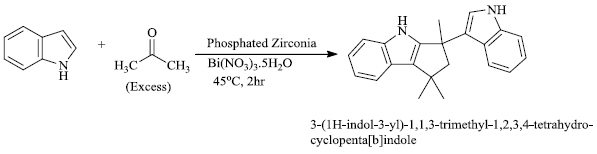
a) S.V. Nadkarniet al. [77] successfully synthesized different substituted cyclo[b]indoles by the use of solid acid catalyst phosphate zirconia (P-Zr) and Bi(NO3)3.5H2O (Scheme 19). The catalytic system used for this process is cheap, efficient and convenient.
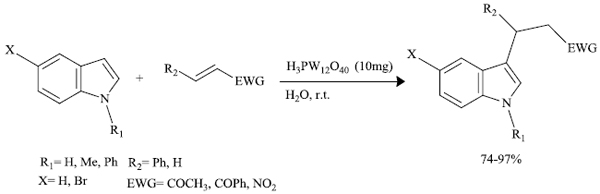
b) M.M. Heravi et al. [78] successfully reported the synthesis of 3-substituted indoles with enhanced properties involving the reaction between indole (or its derivative) and a Michael acceptor in the presence of heteropoly acid (HPA) catalyst like H3PW12O40 (Scheme 20). The products were obtained via Friedel-Crafts alkylation at C3 of indole (or its derivative).
3.5. Preparation of Indole Derivatives (Catalyst-free Conditions)
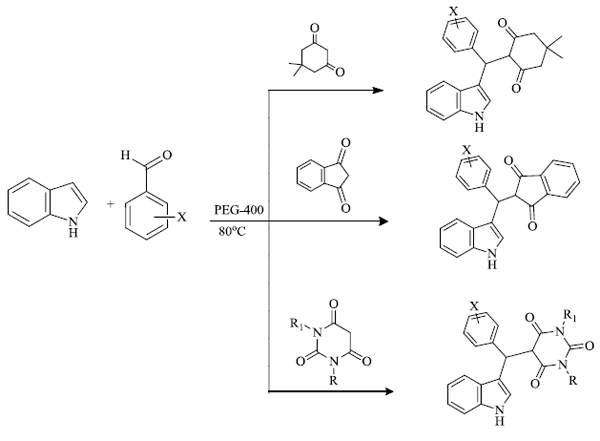
a) R. Kardooni et al. [79] successfully synthesized 3-substituted indoles (yield 86-96%) in 35-80 minutes by the use of MCR process. In this process, polyethylene glycol 400 is treated as a reaction promoter and medium for the reaction between indole and aromatic aldehydes, and C-H activated acids are required for the preparation of desired indole derivatives (Scheme 21). This process is catalyst-free and selective for the production of heterodimer products rather than the formation of homodimer adducts like bisindole/xanthine.
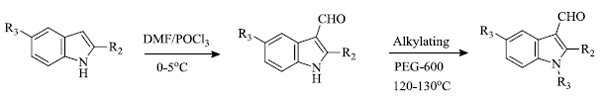
b) A low-cost, fast and environment-friendly methodology was developed by P.K. Dubey et al. [80] for the green synthesis of indole derivatives, especially N-alkyl/aralkyl and indole-3-carboxaldehydes, using polyethylene glycol (PEG-600) (Scheme 22).
c) Y. Yang et al. [81] successfully reported catalyst-free and water as the medium methodology for the preparation of 3-sulfenylindoles without any use of ligand or additive (Scheme 23). Here, thiolation of indoles was carried out with sulfonyl hydrazides to give the desired product(s).
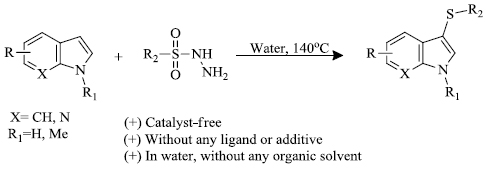
3.6. Synthesis of Indole Derivative using Nanoparticles
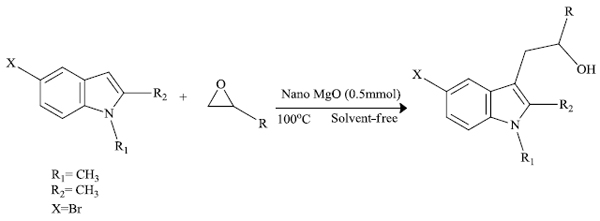
a) M. Hosseini-Sarvari et al. [82] successfully used nano MgO for the production of indole derivatives at the C3 position via Friedel-Craft Alkylation. Under solvent-free conditions, indole upon treatment with epoxides using nanoparticles of magnesium oxide as a catalyst provided bioactive indole derivatives (Scheme 24). Magnesium oxide behaves as an eco-friendly catalyst in this process and can catalyze the ring-opening of epoxide by indole.
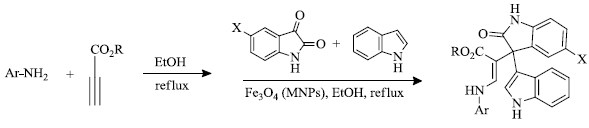
b) H. Hajighasemi et al. [ 83 ] reported the synthesis of 3-Indol-3-yl-oxoindolin-3-yl-3-acrylates by the use of magnetic oxide (III) nanoparticles (Fe 3 O 4 MNPs) (Scheme 25 ). This methodology avoided the application of hazardous substances as solvents and utilization of highly efficient and recyclable catalysts, enabling their convenient separation from the reaction mixture.
3.7. Microwave-assisted Synthesis
There are several processes by which indole and its derivatives can be prepared by using microwave irradiation. The following processes describe MW irradiation-induced preparation of several indole derivatives.
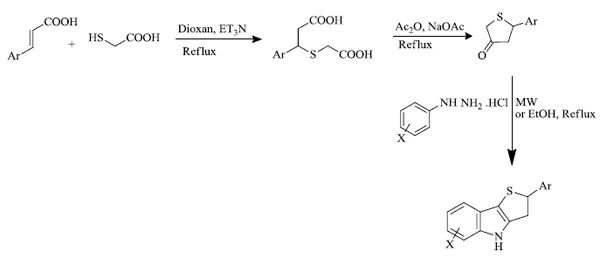
a) S.V. Karthikeyan et al. [ 84 ] prepared 2-aryl-3,4-dihydro-2H-thieno[3,2-b]indoles in good yield through the microwave irradiation method. This method can be regarded as an effective and fast route for the regioselective synthesis of indole derivatives via the Fischer process. It involves the reaction between arylhydrazine hydrochloride and 5-aryldihydro-3(2H)-thiophenones to give desired products in 85-98% yield (Scheme 26 ). This reaction is also performed in EtOH under reflux conditions, but the relative yield is less. The thienoindoles formed exhibited excellent in-vitro antimycobacterial activity.
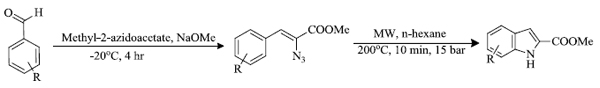
b) F. Lehmann et al . [ 85 ] reported Hemetsberger–Knittel indole synthesis of indole derivatives under MW irradiation. Benzaldehyde or its derivatives are initially converted to alpha-azidocinnamates which then form several indole derivatives by ring closure under microwave irradiation (Scheme 27 ). This method provides an easy and rapid path for the preparation of different derivatives of indoles.
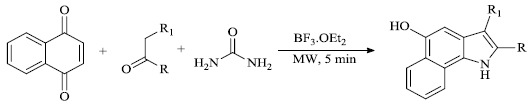
c) One-pot synthesis of benzo-indoles was successfully attained under microwave irradiation by M. Borthakur et al. [86]. Benzo-indoles (Scheme 28) were prepared upon the reaction of omega-substituted-acetophenones with naphthoquinone and urea (Nenitzescu reaction) in solvent-free conditions, eradicating the need for hazardous substances. High yield and enhanced reaction rates were estimated by the use of BF3.OEt2 as the catalyst.
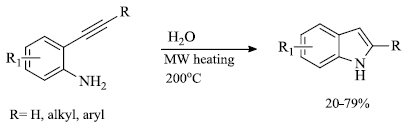
d) A. Carpita et al. [87] demonstrated a simple and convenient way for the preparation of indole derivatives by the use of microwave irradiation. The formation of the desired product was carried out by the microwave-assisted cyclo-isomerization of 2-alkynylanilines using water as a reaction medium catalyzed by inorganic salts like KCl/NaHCO3 (Scheme 29).
CONCLUSION
The study indicates that indole and its derivatives can be prepared by using various methodologies. Conventional methods involve the use of more chemicals, and harsh conditions for the synthesis of the desired product, while synthesis that follows the norms of green chemistry uses mild reaction conditions, less harmful chemicals, efficient catalysts, solvent-free or water-mediated protocols to yield the desired product in high amount and in shorter times. Thus, on the basis of the above information, it has been finalized that the use of ionic liquids and microwave irradiations for the synthesis of novel as well as existing compounds is much better as compared to using conventional methods.
CONSENT FOR PUBLICATION
Not applicable.
FUNDING
None.
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
None.


