Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Macrocyclized Betulin Derivatives as a Novel Class of Anti-HIV-1 Maturation Inhibitors
Abstract
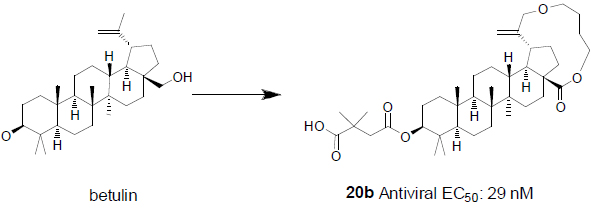
A macrocycle provides diverse functionality and stereochemical complexity in a conformationally preorganized ring structure, and it occupies a unique chemical space in drug discovery. However, the synthetic challenge to access this structural class is high and hinders the exploration of macrocycles. In this study, efficient synthetic routes to macrocyclized betulin derivatives have been established. The macrocycle containing compounds showed equal potency compared to bevirimat in multiple HIV-1 antiviral assays. The synthesis and biological evaluation of this novel series of HIV-1 maturation inhibitors will be discussed.