A Review: Medicinally Important Nitrogen Sulphur Containing Heterocycles
Abstract
Nitrogen sulphur containing heterocycles have specific properties due to which they can be used as a potential material in a different type of industries such as medicinal/pharmaceutical, paint, packing and textile, required for various chemical, physical operations and their use as products. Especially dyes, paint, agrochemicals, medicine, etc. make them more significant. In present days, Nitrogen-Sulfur heterocycles are repeatedly attracting the interest of chemists due to their exceptional bioactive behavior. The present study is a review of the work carried out by a chemist in the discovery of new, effective, medicinally important heterocyclic compounds. The present review basically focused on nitrogen-sulfur heterocycles of potential therapeutic interest, especially with thiazole, thiazine, pyrimidine, morpholine and piperazine heterosystems, benzothiazines, pyrazole-benzothiazines, morpholine-benzothiazines, piperazine-benzothiazines and pyrimidine-benzothiazoles, mainly due to their unique structural features, which enable them to exhibit a number of biological and pharmacological activities. Due to a novel mode of action, a broad spectrum of activity, lesser toxicity towards mammalian cells, and suitable profiles towards humans have triggered the use of Nitrogen Sulphur containing heterocycles in designing and synthesizing their derivatives with better properties. The overall objective of the review is to discuss the importance of novel biodynamic structurally diverse heterocycles of potential therapeutic interest: pyrimidine, morpholine, piperazine, pyrozole, benothiazoles, pyrimidobenzothiazoles, 4H-1,4-benzothiazines, pyrazolyl-benzothiazines, morpholinyl-benzothiazines and piperazinylbenzothiazines in order to have access to important commercial molecules for the search of better future.
1. INTRODUCTION
Heterocycles are considered as the largest section of chemistry, especially organic chemistry. A greater part of the natural compounds produced by biotic component has heterocyclic rings as a constitutional part of their molecules. Different types of commercially important compounds alkaloids like vinblastine, reserpine, morphine, ellipticine, antibiotics like cephalosporin, penicillin etc., cardiac glycosides and different type of pesticides are heterocycles of meaning for animal and human health. The majority of the important advances have been developed by synthesizing new heterocycles which imitate natural products with similar biological activities. For that reason, scientists/researchers/chemist communities are on a nonstop search to develop better pesticides, pharmaceuticals, fungicides, compost material, weed killers, insecticides, etc. Heterocycles' role in biological system is very important. Biochemical processes of components of living organisms like RNA, DNA etc. are based on heterocycles. Except for this present life pattern and civilization, there are additional significant applications of heterocycles in the fields of cosmetics, additives, antioxidants, vulcanization accelerators dyestuffs, photographic material, reprography, data storage, solvents, and plastics. Eventually, heterocyclic chemistry is an infinite supply of exceptional compounds. A large number of models of carbon, heteroatoms and hydrogen, can be produced, which have various biological, physical and chemical properties [1-7]. The expansion of newly discovered processes and the planned use of recognized procedures for the development of heterocycles continue to strengthen the vast domain of organic chemistry.
A specific class of heterocycles having sulfur-nitrogen heteroatoms includes very important aromatic compounds that show physicochemical properties with significance in the development of futuristic materials such as magnets and molecular conductors. At present, interest has been promptly growing in accepting modifications and the characteristics of sulphur-nitrogen based heterocycles. Aromatic heterocycles containing Nitrogen (N) and sulfur(S) are resulting from aromatic carbocycles with the replacement of one or more carbon by a heteroatom in the ring. Whereas, the occurrence of sulfur and nitrogen atoms in the cyclic ring is usually related to the complexity and instability in the synthesis, however, the established nitrogen and sulfur containing heterocycles with significant properties have repeatedly been synthesized. On account of the availability of electrons (unshared pairs) and the distinction in electronegativity between carbon and heteroatoms, heterocycles are very significant in the cyclic molecular structures. Therefore, the nitrogen-sulphur heterocycles exhibit physicochemical properties and reactivity fairly diverse from the precursor carbocyclic compounds [8-12]. The sulphur-nitrogen heterocycles form a fascinating class of heterocycles and inviting the attention of the researchers due to their structural heterogeneity and biomedical properties. In view of the structural modifications with the presence of heteroatoms and the relationship of structures with the pharmacological and biological activities. In this review article, we focused on nitrogen-sulfur heterocycles of biological and pharmacological significance inculcating multi-dimensional structural features due to distinctiveness in substituents, heterocyclic systems and adjoined pharmacologically active functional groups for making them accessible for biological evaluation and SAR (structural activity relationship) studies. In this review, we have focused on nitrogen-sulfur heterocycles of potential therapeutic interest especially with thiazole, thiazine, pyrimidine, morpholine and piperazine heterosystems, benzothiazines, pyrazolylbenzothiazines, morpholinylbenzothiazines, piperazinylbenzothiazines and pyrimidobenzothiazoles, mainly due to their unique structural features, which enable them to exhibit a number of biological and pharmacological activities. The pharmacological/biological activities of heterocyclic compounds mainly depend on the structural specificity and the strength of interaction between a drug and receptors present in the biological system.
2. REVIEW OF LITERATURE
2.1. Medicinally Important Pyrimidine, Benzothiazole Fused Heterosystem: Pyrimidobenzothiazole
Pyrimidine and Thiazole nuclei are treated preferred structures as both these heterocyclic systems constitute the pharmacophore of diverse biological active molecules [13-19] Fig. (1). In medicinal chemistry, the therapeutic applications of pyrimidine derivatives are well known. RNA and DNA activities are based on nucleic acids Uracil, Thymine and cytosine, which have pyrimidine unit. Pyrimidine nucleus compounds acquire a wide variety of biological activities, like stavudine and zidovudine as antiHIV, sulphamethiazine trimethoprim, and sulphadiazine as antibacterial, idoxuridine and trifluoridine as antiviral, barbiturates e.g. phenobarbitone as sedative, 5-fluorouracil as anticancerprazosin and minoxidil as antihypertensive, hypnotics and anticonvulsant, thionzylamine as H1-antihistamine, and fervennuline and toxoflavin as antibiotics, propylthiouracil as antithyroid, sulphadoxin as antimalarial and antibacterial, etc [20]. Pyrimidine and their derivatives are very well known anti-inflammatory, analgesic and antipyretic agents [21-33].
In the same way, substituted benzothiazoles show interesting biological activities, like antiviral, anti-inflammatory, anticonvulsant, antitumor, antimicrobial and antagonists, etc [34-45]. The adjoining of one biodynamic heterocyclic system with another biodynamic heterosystem results in a molecule with structural variability and improved pharmacological activity. The fusion of heterosystems has been proven to be useful and attractive for the design of new molecular framework of therapeutically interesting drugs. With the object of discovery of exploring new heterocyclic therapeutics, we focused on pyrimidobenzothiazoles, a new class of heterocycles, incorporating two pharmacologically important heterocyclic systems, benzothiazole and pyrimidine [46-56].
Pyrimidobenzothiazoles reportedly exhibited an extensive choice of pharmacological and biological activities such as anticonvulsant [57], anti-inflammatory [58], antitumor [59], etc. Pyrimidobenzothiazoles can also act as GABA receptor binding agents [60-62].
2.2. Biodynamic Heterosystem: Benzothiazine and their Derivatives
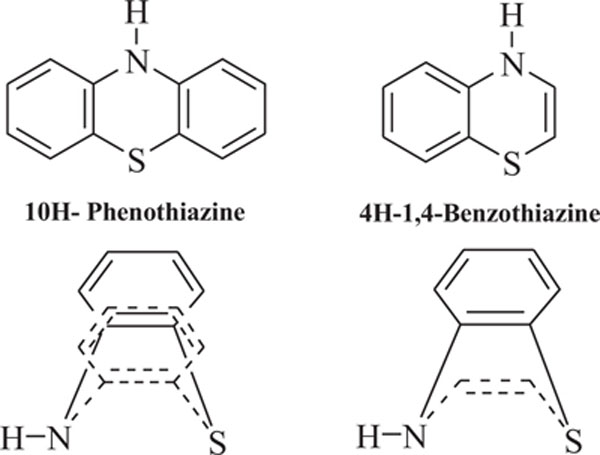
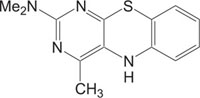
Benzothiazines are structural analogues of phenothiazines [63-69] and exhibit similar structural flexibility along with structural specificity, fold along nitrogen and sulfur axis, as in phenothiazines. The direction of folding and the magnitude of folding angle depend to a larger extent on the position as well as the type of the other substituents on the ring system, which consequently affect the therapeutic activities considerably. The structural specificity along nitrogen-sulfur axis in phenothiazines and 4H-1,4-benzothiazines has been considered as a significant factor to be responsible for their activities and made both the series important from not only structural point of view but also from pharmacological as well as industrial view point [70-72]. The structural presentation of phenothiazine and 4H-1,4-benzothiazine ring systems according to Gordon’s model is presented to show the structural similarity of both the heterosystems Fig. (2).
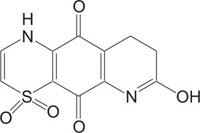
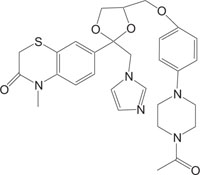
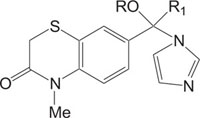
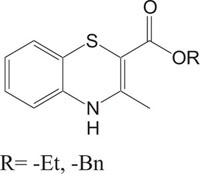
Benzothiazines have also been established for their pharmacological/biological behavior such as antihypertensive [73], antiinflammatory [74], antianginal [75], antihistaminic [76], antipsychotic [77], antiemetic [78], neuroleptic [79], antibacterial [80], antioxidant properties [81], etc. 4H-1,4-Benzothiazines have also been used as colour photographic developers and dye stuffs in the industry [82-84]. Some 4H-1,4-benzothiazines along with their biopharmaceutical activities are presented in Table 1.

| Nitrogen-Sulphur Containing Heterocycles | Activity | Reference |
|---|---|---|
 |
Vasorelaxant/ KATP-Channel Openers | [85] |
 |
Anti-rheumatic Anti-proliferate |
[86] |
 |
Vasorelaxant | [87] |
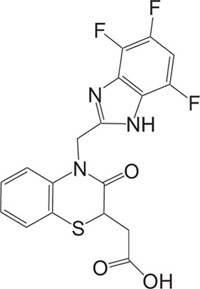 |
Antidiabetic | [88] |
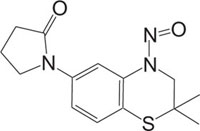 |
KATP Channel Openers Vasorelaxant |
[89] |
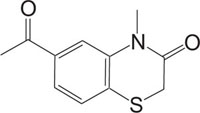 |
Apoptosis | [90] |
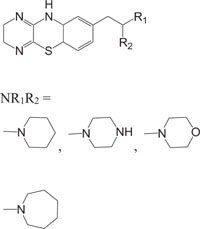 |
Intercellular adhesion molecule-I (Icam-I) | [91] |
 |
Intercellular adhesion molecule-I (Icam-I) | [92] |
 |
Anti-inflammatory | [93] |
 |
Antimalarial (Against a rodent malaria parasite Plasmodium berghei) | [94] |
 |
Lipoxygenase inhibitor | [95] |
 |
Antimicrobial (Antibacterial activity against Bacillus subtilis, Bacillus mega, Escherichia coli, Aspergillus arogens and antifungal activity against Aspergillus awamori) | [96] |
 |
Anti-Candida | [97] |
 |
Antifungal against Candida albicans | [98] |
 |
Antagonistic | [99] |
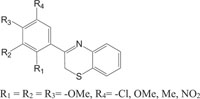 |
Antibacterial against Staphylococcus aureus | [100] |
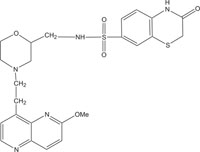 |
Antibacterial against Neisseria gonorrhoea | [101] |
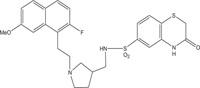 |
Antimicrobial against Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Streptococcus pyogenes, Enterococcus faecalis and Enterococcus faecium | [102] |
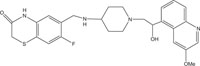 |
Antimicrobial against Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pneumoniae | [103] |
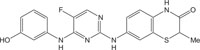 |
Anti-autoimmune | [104] |
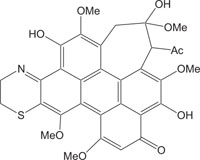 |
Antitumor, anti HIV | [105] |
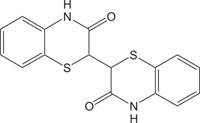 |
Natural pigments | [106] |
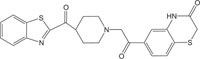 |
Antimicrobial against S. aureus | [107] |
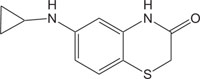 |
Renin Inhibitor | [108] |
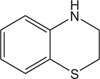 |
Antiviral against zika virus | [109] |
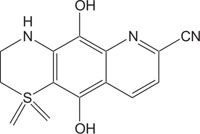 |
Anti-inflammatory | [110] |
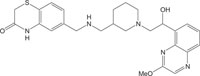 |
Antimicrobial against staphylococci, pneumococci and enterococci | [111] |
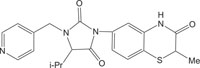 |
Kinase Inhibitor | [112] |
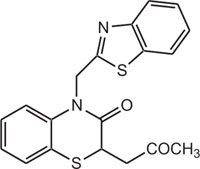 |
Gaba Brian receptor | [113] |
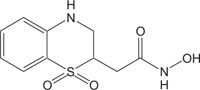 |
Antimicrobial against Staphylococcus, Enterococcus, Streptococcus, Haemophilus, Moraxella, Escherichia, Mycobacterium, Mycoplasma, Pseudomonas, Chlamydia, Rickettsia, Klebsiella, Shigella, Salmonella, Bordetella, Clostridium, Helicobacter, Campylobacter, Legionella or Neisseria. | [114] |
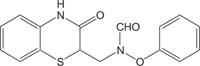 |
Antibacterial | [115] |
 |
Anti-obesity | [116] |
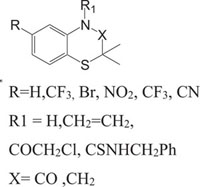
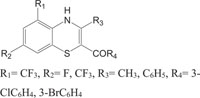
2.3. Pharmaceutically Important Pyrazole Derivatives: Pyrazolylbenzothiazine
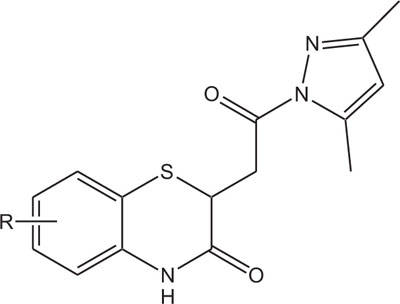
Pyrazole derivatives, a set of hererocycles, occupy a significant place in pesticide and medicinal chemistry by means of a large collection of bioactivities. Pyrazole derivatives are well known and reported to show antibacterial, fungicidal, herbicidal, antimicrobial, antiinflammatory, and anticancer activities [117-127]. Pyrazophos, the fungicide was marketed by Hoechst AG in1974, which have the ability to control powdery mildew in vegetables. The significance like a novel mode of action, broad spectrum of activity, lesser toxicity towards mammalian cells, and suitable profiles towards humans have triggered the use of pyrazole in designing and synthesizing its derivatives with better properties. Recently, pyrazole compounds, like pyraclostrobin (BASF, 2001) and penthiopyrad (Mitsui Toatsu Chemicals, 1995), are found to be latent antifungal agents for the control of various plant diseases. In recent years, researchers have given considerable attention to the synthesis of pyrazole and their derivatives due to their wide ranging bioactivities obtained through modification of structural profile by a change of the substituents in pyrazole ring [128].
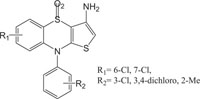
In view of the structural relationship with bioactivities, the synthesis of substituted 1,4-benzothiazines Fig. (3), incorporating both benzothiazine and pyrazole heterosystems with this assumption that the synthesized heterocycles will exhibit better features caused by co-existence of two types of pharmacophoric interactions with different action of mechanism have also been reported.
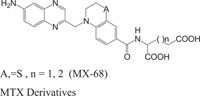
2.4. Medicinally Important Morpholine/Piperazine and their Derivatives: Morpholinyl/Piperazinylbenzothiazines
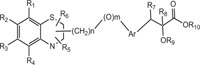
The systems containing morpholine fragments have attracted interest as potential biologically active compounds [129-135]. Morpholines show a wide spectrum of properties varying from medicinal field applications to agricultural use [136]. Reboxetine acts as an antidepressant drug and is applied to treat panic disorder, clinical depression, hyperactivity disorder [137]. Fenpropimorph is a broadly used leaf fungicide and is predominantly used to limit fungal diseases in cereals [138]. Trioxazine, ofloxacin, ethmosine, dextromoramide, etc. containing morpholine nucleus have also found their applications in medicine. Morpholine derivatives have been the area of interest for the pharmaceutical industry as these act as bioactive compounds and effective substrates for further elaboration. In this regard, a number of patents elucidating the biological significance of such compounds have been published [139-143]. The literature survey reveals that the compounds with morpholine Fig. (4) show enormous therapeutic uses that include antimalarial [144], antibacrerial [145], antimicrobial [146], anticonvulsant agents, antidepressant [147], lukemia [148], tranqulizer s [149] and antituberculous agents [150].
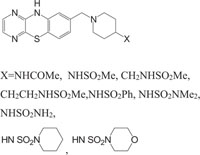
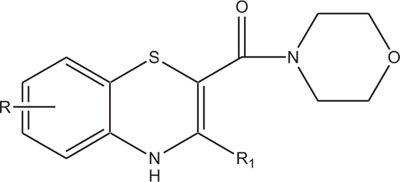
Similarly, the piperazine ring is a preferrable heterosystem in medicinal-pharmaceutical chemistry and is frequently found in the structure of various enzyme inhibitors as well as clinical therapeutics [151]. Piperazine and its derivatives act as useful synthetic building blocks and have been regularly used in the preparation of important biologically active compounds. Piperazine and its derivatives have also been shown to exhibit a wide spectrum of pharmacological and biological activities such as, antibacterial [152, 153], antineoplastic [154], antinociceptive [155], antimalarial [156], antiproleferative activity [157], Na channel blocker [158], antitumor [159], antagonistic [160], antimicrobial [161], etc.
Taking into account the significance of piperazine scaffold in a wide range of applications [162-174], we apprehended that it might be worthwhile to incorporate the piperazine heterosystem alongwith 1,4-benzothiazine Fig. (5), to synthesize therapeutically interesting heterocycles with structural diversity [175-179].

CONCLUSION
Literature reveals that nitrogen and sulphur containing heterosystems are truly important for the development of human and associated society. These heterosystems play an important and key role in curing process against life threating diseases, which directly influence the growth of humans and animals. The overall objective of the review is to discuss the importance of novel biodynamic structurally diverse heterocycles of potential therapeutic interest, pyrimidine, morpholine, piperazine, pyrozole, benothiazoles, pyrimidobenzothiazoles, 4H-1,4-benzothiazines, pyrazolyl-benzothiazines, morpholinyl-benzothiazines and piperazinylbenzothiazines in order to have access to important commercial molecules for the search of better future.
CONSENT FOR PUBLICATION
Not applicable.
FUNDING
None.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare no conflict of interest, financial or otherwise.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Declared none.


